Are you curious about hydroponics and eager to learn all the essential details? Look no further! This beginner’s guide to hydroponics will give you the knowledge you need to get started on your hydroponic gardening journey. Whether you have a green thumb or just want to explore a new way of growing plants, this guide will provide you with the basics of hydroponics and equip you with the necessary information to successfully grow plants without soil. From understanding the principles of hydroponics to setting up your hydroponic system, we’ve got you covered. Get ready to embark on an exciting adventure in the world of hydroponics!
What is Hydroponics?
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil. Instead of drawing nutrients from the ground, plants receive a carefully balanced nutrient solution delivered through water. Depending on the system, roots may be suspended directly in the solution or supported by an inert growing medium (such as rockwool, perlite, coco coir, or clay pebbles) while nutrients are supplied through irrigation.
Because growers can control water, nutrients, and oxygen at the root zone, hydroponics is widely used in greenhouses and indoor farms where consistency and efficiency matter. Many growers choose hydroponics for practical reasons: it can reduce water waste, make better use of limited space, and support year-round growing when temperature and lighting are managed.
Definition of Hydroponics
Hydroponics is a soilless cultivation method in which plants receive essential mineral nutrients through a water-based nutrient solution. The term “hydroponics” is commonly explained as coming from Greek roots “hydro” (water) and “ponos” (work), reflecting the central role of water and nutrient delivery in the growing process.
Brief History of Hydroponics
Although hydroponics is often described as modern, water-based cultivation has been practiced in various forms for centuries. Some ancient agricultural methods are sometimes compared to hydroponics because they relied on water management and intensive production, though they are not the same as modern nutrient-solution systems.
Modern hydroponics developed through scientific research into plant nutrition and controlled cultivation, and it became widely adopted in the 20th century alongside greenhouse production and, later, indoor growing technologies.
Benefits of Hydroponics
Hydroponics offers several exciting advantages over traditional soil-based farming methods. Let’s explore some of the key benefits below.
Water Conservation
One of the most significant advantages of hydroponics is its water efficiency. Traditional soil-based agriculture consumes large amounts of water due to evaporation, inefficient irrigation practices, and water runoff. In hydroponics, water is recirculated within the system, resulting in up to 90% less water usage compared to traditional farming methods. This makes hydroponics an environmentally-friendly choice, particularly in regions facing water scarcity.
Space Efficiency
In today’s world, where urban spaces are becoming increasingly limited, hydroponics provides a solution for growing plants in compact areas. Hydroponic systems can be set up vertically or in small indoor spaces, allowing for maximum use of space. This makes hydroponics particularly advantageous for urban gardens, rooftop farming, or even indoor gardening setups.
Year-round Growing
Unlike traditional agriculture, hydroponics enables year-round crop production regardless of the season or climate. By providing plants with optimal growing conditions, such as temperature, light, and nutrient levels, hydroponics allows for uninterrupted cultivation. This is especially beneficial for regions with extreme climates or limited growing seasons, ensuring a consistent supply of fresh produce throughout the year.
Improved Plant Growth and Yield
Hydroponics provides plants with direct access to essential nutrients, resulting in accelerated growth rates and increased yields. In a controlled environment, plants can receive an optimum balance of nutrients, promoting healthy root development and robust foliage. With proper monitoring and care, hydroponic crops consistently exhibit higher productivity and improved quality compared to traditional soil-grown plants.
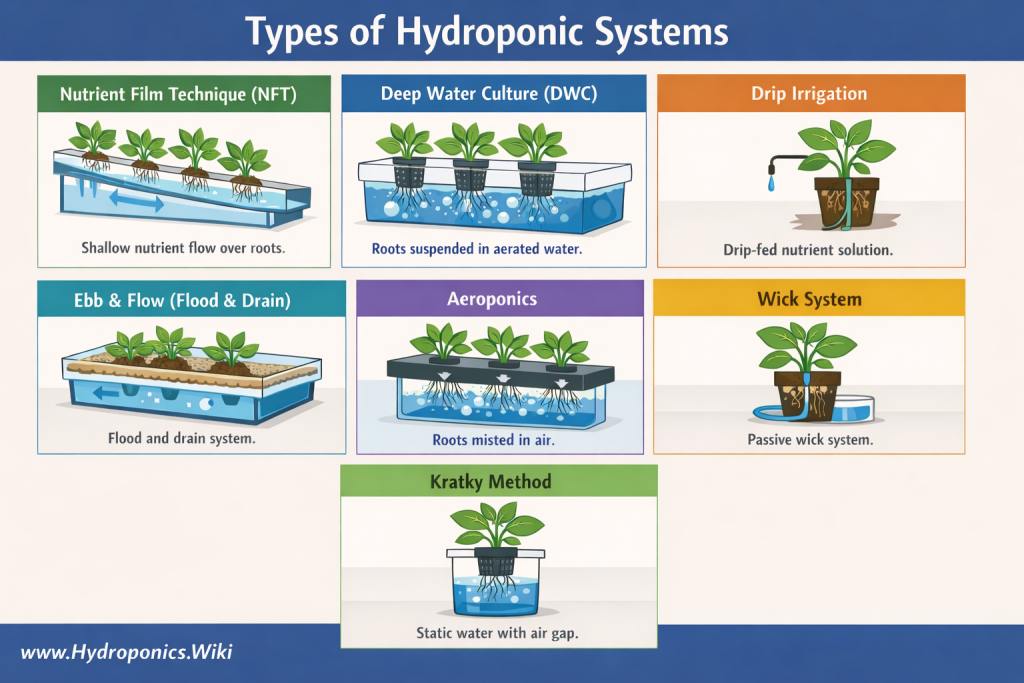
Types of Hydroponic Systems
Hydroponic systems come in several common designs. The best choice depends on your space, budget, crop type, and how much hands-on monitoring you want to do. Below are popular systems, what they’re best for, and key considerations.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
NFT uses a continuous flow of a shallow “film” of nutrient solution through sloped channels so roots receive water and nutrients while remaining partially exposed to air. NFT is commonly used for fast-growing, shallow-rooted crops such as lettuce and many herbs, and it is also used for strawberries in some setups. Because roots can dry quickly if flow stops, NFT systems typically require reliable pumps, good filtration, and attention to clogging or root overgrowth.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Deep Water Culture grows plants with roots suspended directly in an aerated nutrient solution. In raft-style DWC, plants sit in net pots supported by a floating raft, while an air pump and air stones provide dissolved oxygen. Raft DWC is especially popular for leafy greens and herbs. Larger fruiting plants can be grown in DWC as well, often using individual buckets or recirculating DWC (RDWC) designs that provide more support and nutrient stability for heavy-feeding crops.
Drip Irrigation
Drip hydroponics delivers nutrient solution to each plant through drip emitters on a schedule (often using a timer-controlled pump). Systems can be recirculating (runoff returns to the reservoir) or drain-to-waste (runoff is discarded). Drip setups are flexible and scale well, making them common in home gardens and commercial greenhouses—especially for larger plants grown in media such as coco coir, perlite, or clay pebbles.
Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
Ebb and Flow, also called Flood and Drain, periodically floods a grow tray or container with nutrient solution and then drains it back into a reservoir. This cycle provides roots with nutrients during the flood phase and oxygen as the solution drains away. Ebb and Flow systems are popular because they work well with many plant types and growing media, and they can be relatively simple to build at home. Key considerations include using a reliable timer and preventing issues like uneven flooding, algae growth, or root saturation if cycle timing is not well matched to the crop and environment.
Aeroponics
Aeroponics suspends roots in air and delivers nutrients as a fine mist or spray. The high oxygen exposure can support rapid growth when conditions are stable, but aeroponics is typically more technical and less forgiving than other systems. Consistent misting, clean water, and well-maintained nozzles are critical, since interruptions can dry roots quickly. Aeroponics is often used for propagation, leafy greens, and research-scale or specialty cultivation.
Wick System
The wick system is a simple, low-maintenance approach that uses wicks and capillary action to draw nutrient solution from a reservoir into the growing medium. Because it is passive (no pump required), it can be a good entry point for beginners and small herb/leafy setups. Its main limitation is delivery rate: it can struggle with larger plants or heavy feeders that need more water and nutrients than the wick can supply.
Kratky Method
The Kratky method is a passive form of hydroponics that grows plants in a container of nutrient solution without pumps or aeration. As the plant consumes water, the solution level drops, creating an air gap that supplies oxygen to the upper portion of the roots while the lower roots remain in the nutrient solution. Kratky is popular for its simplicity and low cost, especially for leafy greens and herbs in small-scale or home setups. It is less ideal for long-duration or heavy-feeding crops unless the system is carefully sized or topped off, since nutrient strength, pH, and oxygen availability can drift over time.
Essential Components of a Hydroponic System
To set up a successful hydroponic system, several key components are required. Let’s go over each essential component in detail.
Growing Medium
In hydroponics, a growing medium replaces traditional soil and provides support for the plants’ root systems. Commonly used growing mediums include perlite, vermiculite, coconut coir, rockwool, and clay pellets. The choice of growing medium depends on factors such as water retention, aeration, and pH stability.
Nutrient Solution
The nutrient solution is a vital component of hydroponics, as it provides all the essential elements necessary for plant growth and development. The solution consists of water mixed with a balanced blend of macro and micronutrients. Commercial nutrient solutions are available, or growers can formulate their own by following specialized hydroponic nutrient recipes.
Water Pump
A water pump is required to circulate the nutrient solution throughout the hydroponic system. The pump ensures that the plants’ root systems have constant access to the required nutrients, preventing stagnation or nutrient depletion.
Reservoir
The reservoir serves as a storage tank for the nutrient solution. It should be large enough to hold an adequate supply of nutrient solution, ensuring a consistent flow to the plants. The reservoir should be lightproof to prevent algae growth and insulated to maintain the desired temperature.
pH Test Kit
Monitoring and maintaining the pH level of the nutrient solution is crucial for optimal plant growth. A pH test kit or pH meter is necessary to regularly measure and adjust the pH levels within the recommended range for specific plant types. This helps ensure correct nutrient uptake and prevents nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
Air Pump
In hydroponics, oxygenation of the root zone is essential for healthy plant growth. An air pump, coupled with air stones or diffusers, introduces oxygen into the nutrient solution, preventing root suffocation and promoting vigorous root development.
Light Source
Since hydroponic systems can be set up indoors or in areas with limited natural light, a supplementary light source is necessary. High-quality grow lights, such as LED or fluorescent lights, provide the necessary spectrum and intensity of light for photosynthesis. The choice of light source should be based on the specific requirements of the plants being grown.
Timer
A timer is essential to automate the lighting and watering cycles in a hydroponic system. It ensures plants receive consistent light and nutrient distribution, depending on their growth stage, helping establish a regular routine and promoting optimal growth.
Choosing the Right Plants for Hydroponics
Hydroponics opens up a world of possibilities for the types of plants that can be successfully grown. However, certain plants tend to thrive better in hydroponic systems than others. Here are some plant categories known to perform well in hydroponics:
Herbs
Herbs such as basil, cilantro, parsley, mint, and rosemary are excellent candidates for hydroponics. They have compact root systems, fast growth rates, and high demand in culinary applications. Growing herbs hydroponically ensures a constant supply of fresh, flavorful leaves for your kitchen creations.
Leafy Greens
Lettuce, spinach, kale, and other leafy greens are well-suited for hydroponic cultivation. Their shallow root systems thrive in NFT or DWC systems, and they exhibit fast growth rates, allowing for quick harvests. Leafy greens grown hydroponically are often more vibrant, pest-free, and nutrient-dense than their soil-grown counterparts.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a popular choice for hydroponic enthusiasts due to their exceptional flavor and high market value. Hydroponic tomato plants typically produce larger, juicier fruits compared to those grown in soil. However, they require adequate support systems and sufficient light and space to thrive.
Strawberries
Hydroponics provides an ideal environment for growing strawberries, allowing for elevated yields and enhanced fruit quality. Strawberries grown hydroponically tend to be sweeter, juicier, and free from soil-borne pests and diseases. This makes them a delightful addition to any hydroponic garden.
Peppers
Peppers, both sweet and hot varieties, are well-suited for hydroponics. They respond favorably to the controlled environment provided by hydroponic systems, resulting in higher yields and more consistent fruit quality. Peppers also benefit from increased nutrient availability, producing vibrant fruits with intense flavors.
Setting Up a Hydroponic System
Setting up a hydroponic system requires careful planning and consideration. Here are the key steps to follow in order to establish a successful hydroponic garden:
Selecting the Location
When choosing the location for your hydroponic system, consider factors such as available space, lighting conditions, temperature, and accessibility for maintenance. Indoor locations or controlled environments like greenhouses provide the advantage of year-round cultivation and full control over environmental variables.
Choosing the System Type
Based on your available space, budget, and desired plants, select the appropriate hydroponic system that suits your needs. Consider factors such as system complexity, plant support requirements, and your level of experience as you decide between NFT, DWC, drip irrigation, aeroponics, or the wick system.
Building or Buying a System
Once you have selected the system type, you can choose to either build your own hydroponic setup or purchase a pre-made system. Building your own system allows for customization and can be a cost-effective option, especially for small-scale setups. Alternatively, purchasing a ready-to-use system can save time and provide a hassle-free start to your hydroponic journey.
Installing the System
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions or the design plan for your DIY system to set up the various components of your hydroponic system. This typically involves connecting the pump, reservoir, tubing, and other elements, ensuring a secure and leak-free installation.
Setting Up Lighting and Timer
Position your grow lights at an optimal height and angle for maximum light distribution. Set up the timer according to the lighting requirements of your plants, providing them with the appropriate photoperiod for each growth stage.
Mixing and Adjusting the Nutrient Solution
Prepare the nutrient solution by following the instructions provided with your chosen nutrient product or recipe. Measure and adjust the pH and nutrient levels using the pH test kit and appropriate nutrient additives, ensuring that the solution meets the specific requirements of your chosen plants.
Monitoring and Maintaining a Hydroponic System
To ensure the long-term success of your hydroponic system, regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial. Here are some key aspects to pay attention to:
Regular pH and EC Testing
Monitor the pH and electrical conductivity (EC) of the nutrient solution on a regular basis using a pH test kit and an EC meter. Adjust the pH as needed to maintain the optimal range for your plants. The EC reading provides an indication of nutrient strength and allows for adjustments if any deficiencies or imbalances are detected.
Water Level Monitoring
Check the water level in the reservoir regularly, ensuring that it remains at the appropriate level. Refill the reservoir with fresh water or top up the nutrient solution as required to maintain adequate levels for plant uptake.
Cleaning and Sanitizing
Keep your hydroponic system clean and free from algae, pests, and diseases. Regularly clean and sanitize the reservoir, pumps, tubing, and any other components to prevent contamination and ensure a healthy growing environment for your plants.
Pruning and Trellising
As your plants grow, regularly prune and train them to maintain proper airflow, prevent overcrowding, and support optimal growth. Trellis larger plants like tomatoes or peppers to provide adequate support and prevent plants from bending or breaking under the weight of fruits.
Managing Temperature and Humidity
Maintaining appropriate temperature and humidity levels is essential for healthy plant growth. Monitor these parameters using thermometers and hygrometers and adjust as necessary to provide an optimal environment for your plants. Adequate ventilation and air circulation also play a significant role in preventing the risk of disease or pests.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Even with proper care, hydroponic systems can encounter various challenges. Here are some common issues you may encounter and tips for troubleshooting:
Nutrient Deficiencies
Monitor your plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies, such as yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or necrotic spots. Adjust the nutrient solution according to the nutrient deficiency’s specific requirements, ensuring the appropriate balance of macronutrients and micronutrients.
Pests and Diseases
Although hydroponics minimizes the risk of soil-borne pests and diseases, it is not immune to these issues. Regularly inspect your plants for signs of pests or diseases and take appropriate measures, such as using organic pest control methods or implementing preventive measures like quarantine for new plants.
Root Rot
Root rot is a common fungal disease that affects the roots of plants, causing them to become slimy, discolored, and mushy. To prevent root rot, ensure proper oxygenation of the root zone, avoid overwatering, maintain a clean system, and consider using beneficial bacteria or fungicides to suppress fungal growth.
Algae Growth
Algae growth in a hydroponic system can clog tubing and create a breeding ground for pests. Prevent algae by keeping the reservoir lightproof and controlling light exposure to the nutrient solution. Use algae inhibitors or UV sterilizers to combat existing algae growth and prevent its recurrence.

Harvesting and Enjoying Hydroponic Produce
The joy of hydroponics lies in the ability to harvest and enjoy your fresh produce. Here are some important considerations for harvesting:
Determining Harvest Time
Each plant has its own timeline for maturity, so it’s important to research and understand the specific harvest time for each crop you are growing. Observe the plant’s growth stage, inspect the fruits or leaves for the desired size or color, and follow the recommended guidelines for optimal harvest timing.
Proper Harvesting Techniques
When harvesting hydroponically grown produce, use clean, sharp tools to avoid damaging the plants. Handle fruits or leaves carefully to prevent bruising or breakage. Proper techniques for each plant variety can vary, so consult reliable resources or gardening experts for specific instructions.
Storing and Using the Harvested Produce
Utilize your freshly harvested hydroponic produce to enjoy its maximum flavor and nutritional value. Store leafy greens or herbs in airtight containers in the refrigerator, while fruits like tomatoes or peppers are best enjoyed at room temperature. Explore various culinary possibilities, such as salads, stir-fries, or smoothies, to make the most of your harvest.
Expanding Your Hydroponic Knowledge
Hydroponics is a continuously evolving field, and there’s always more to learn. Here are some ways to expand your hydroponic knowledge:
Joining Hydroponic Communities
Connect with fellow hydroponic enthusiasts by joining online forums or social media groups dedicated to hydroponics. Engage in discussions, ask questions, and share your experiences to gain insights and build a supportive network.
Attending Workshops and Classes
Local gardening centers, agricultural universities, or hydroponic suppliers often offer workshops or classes on hydroponics. Take advantage of these opportunities to learn from experts, gain hands-on experience, and stay up to date on the latest techniques and technologies.
Reading Hydroponic Books and Resources
There are numerous books, articles, and online resources available that delve into every aspect of hydroponics. From beginner’s guides to advanced cultivation methods, these resources provide comprehensive information and guidance to enhance your hydroponic journey.
By embracing hydroponics, you’re embarking on an exciting path to sustainable and productive gardening. With the right knowledge, equipment, and dedication, you can enjoy the benefits of hydroponics and cultivate flourishing plants at any time of the year. So, roll up your sleeves and get ready to grow an abundant and vibrant hydroponic garden!
© 2025 by Hydroponics.wiki, All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without prior written permission.
